
All The Parts of a Guitar Explained With Diagram
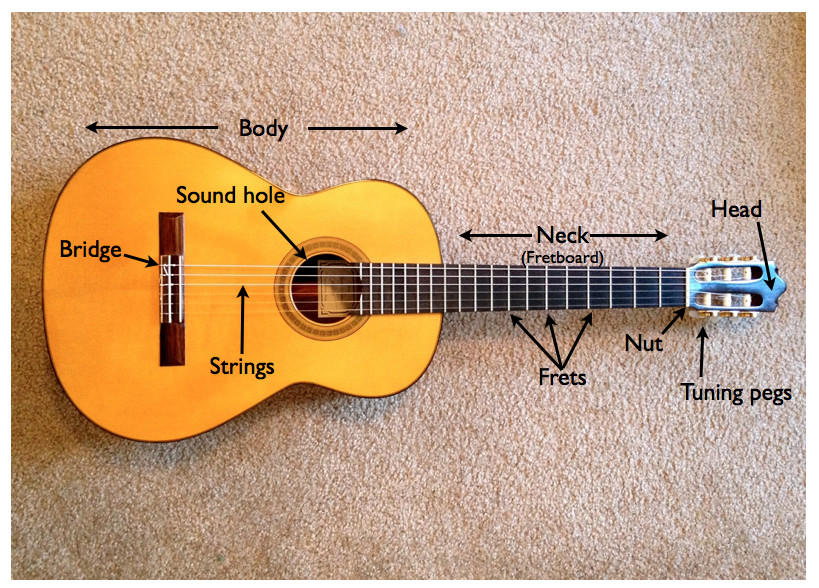
Headstock. A classical guitar's headstock (also known as a peghead) is located at the top of the guitar and is primarily used to house the tuning keys. It is connected to the guitar's neck and is used to hold all 6 strings in place. Generally speaking, the headstock on a classical guitar will contain the tuning keys, string rollers and the nut.

Guitar Bender The parts of a guitar
The nut impacts your guitar's overall playability and tone, one of the more underrated parts. The nut will enable proper string spacing, string height, action, and even string durability. It can also help you eliminate fret buzz. The most common materials found in nuts include bone, ivory, metal, plastic, ebony, and graphite.
Parts of an Acoustic Guitar Photo Guide
Parts of the Guitar Body The body is the main bulk of the instrument. As the main bulk of the guitar, it's arguably the most important component and plays a large role in the overall tone, especially with acoustics.
Guitar Parts (lesson)
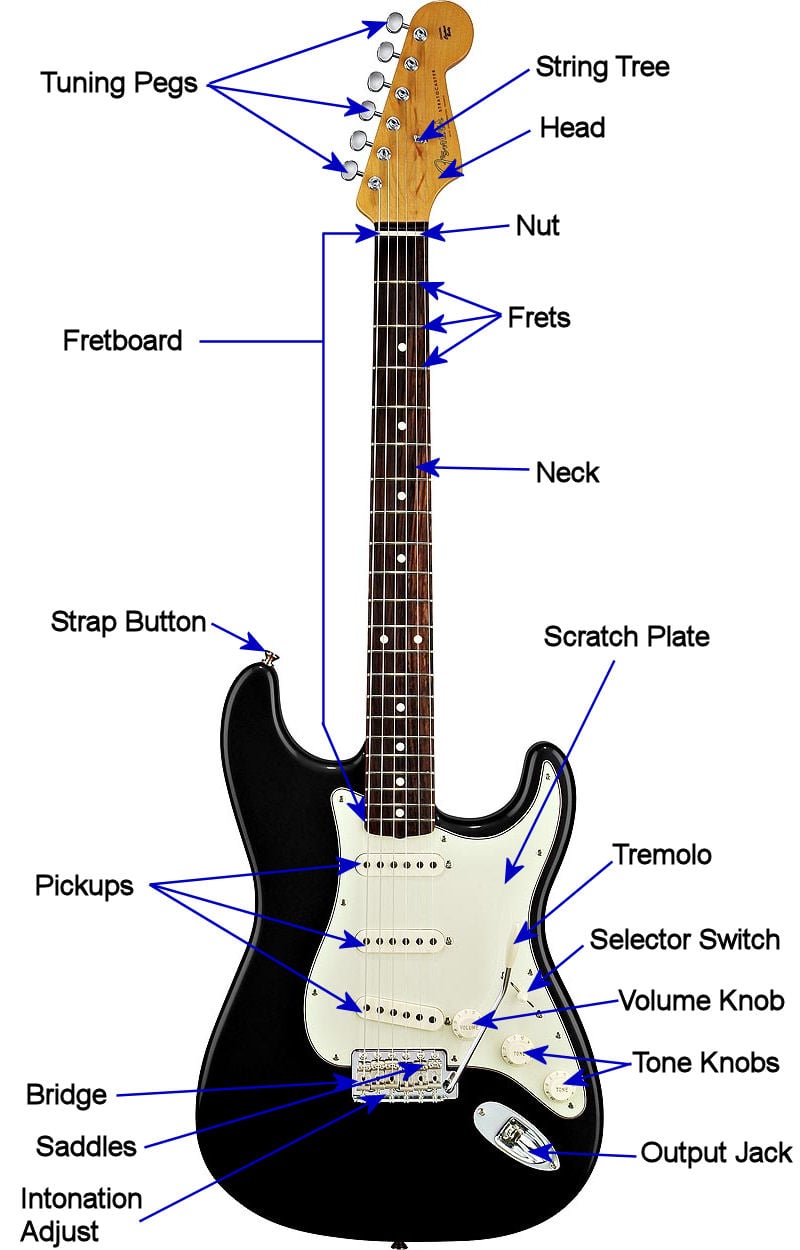
2. Tuning Peg. The Tuning Peg is integral to the guitar presented on the sides, also known as Machine heads. There are 6 tuning pegs - 3 to the right and 3 to the left. With the tuner's help, these tuning keys are twisted in a certain way to set the intonation. The tuning is also known as Standard Tuning. 3.

Parts of acoustic and electric guitar labeled structure vector illustration Guitar, Electric
Parts of the Acoustic Guitar Explained O.k. now let's look a little bit more in-depth into the individual parts of the acoustic guitar. Some of this will be a little bit technical for some or obvious for others. Headstock The headstock is the very top of the guitar and houses the machine heads. Machine Heads The machine heads are very important.

Basic Knowledge of Guitar
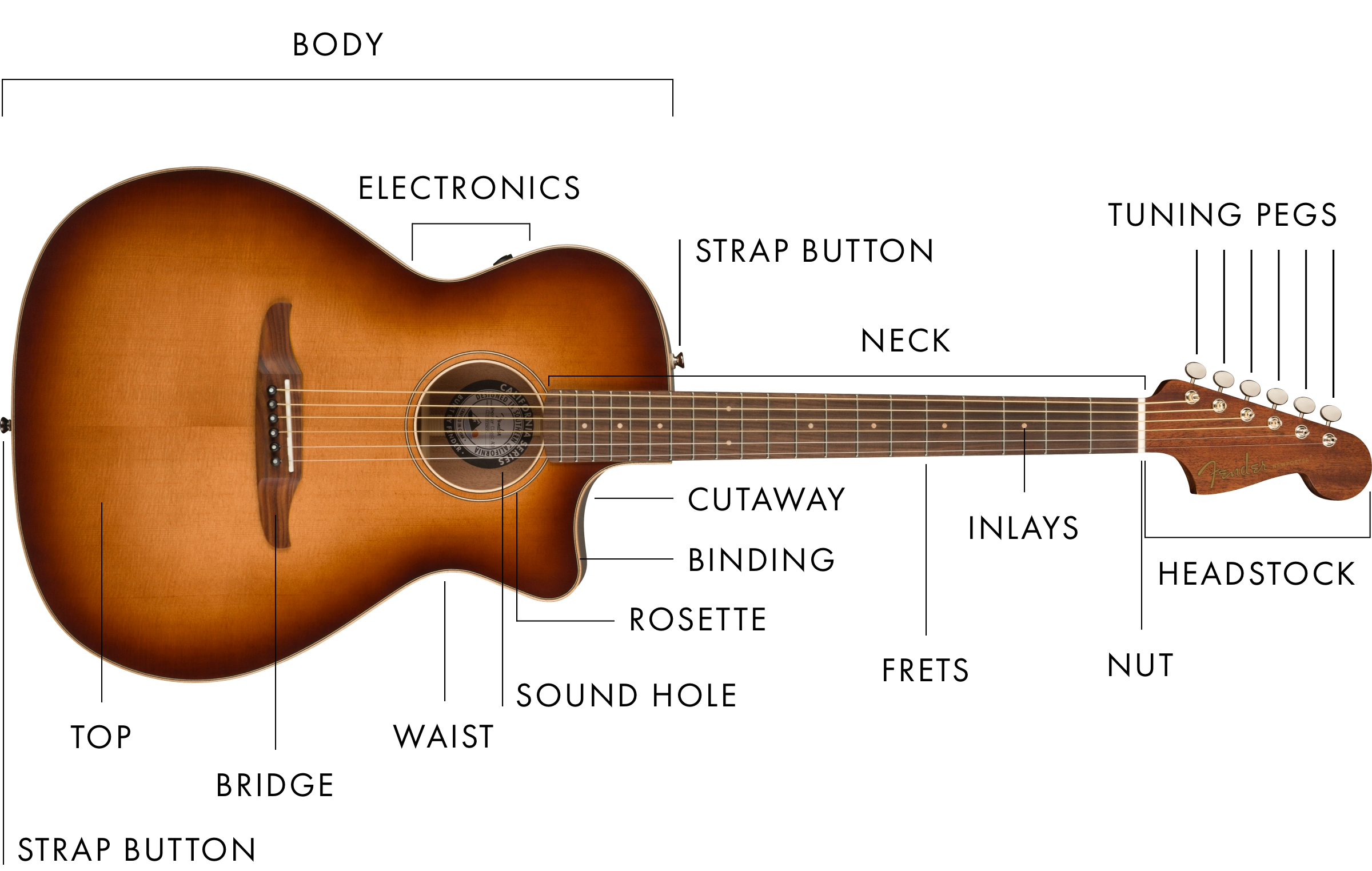
Without further ado, below is a labeled diagram that shows the various components of an electric and acoustic guitar. Head The head's primary purpose is to hold the tuning mechanisms/gears and ends of the strings. Do you know that the guitar's resonance is also transmitted through the head when the guitar is played? Try this.
Acoustic Guitar Labeled Parts Self Taught Guitar Lessons
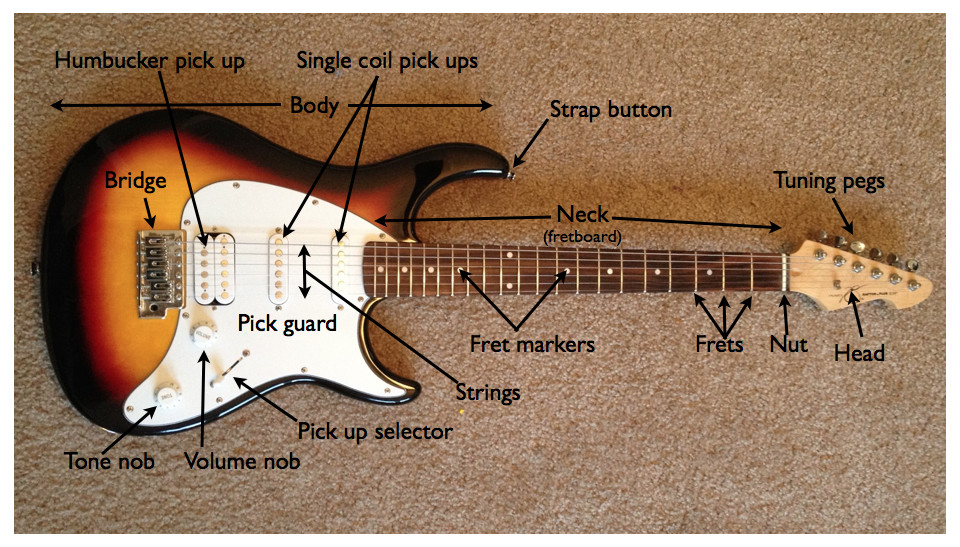
Electric guitar strings are made out of metal, such as nickel-plated steel, and when you pluck the strings, the vibration is translated into an electrical signal that the pickups can then translate into sound. The types of strings you use can have a big impact on the sound, such as round wound vs. flat wound.
Acoustic Guitar Parts Diagram
4. Head -The head holds the tuners. The design of the head determines the placement and design of the tuners also. 5. The nut - The nut of the guitar holds the strings in place on the neck. The material the nut is made of affects the sound of the guitar and it can be made of a variety of materials from fossilized mammoth bone to plastic.
Electric Guitar Labeled Parts Self Taught Guitar Lessons
The Parts of a Guitar Generally speaking, there are two types of guitars: acoustic and electric. Luthiers, or guitar makers, build acoustic guitars so they can be played without amplification. Electric guitars require an amplifier to produce a sound loud enough to hear well.
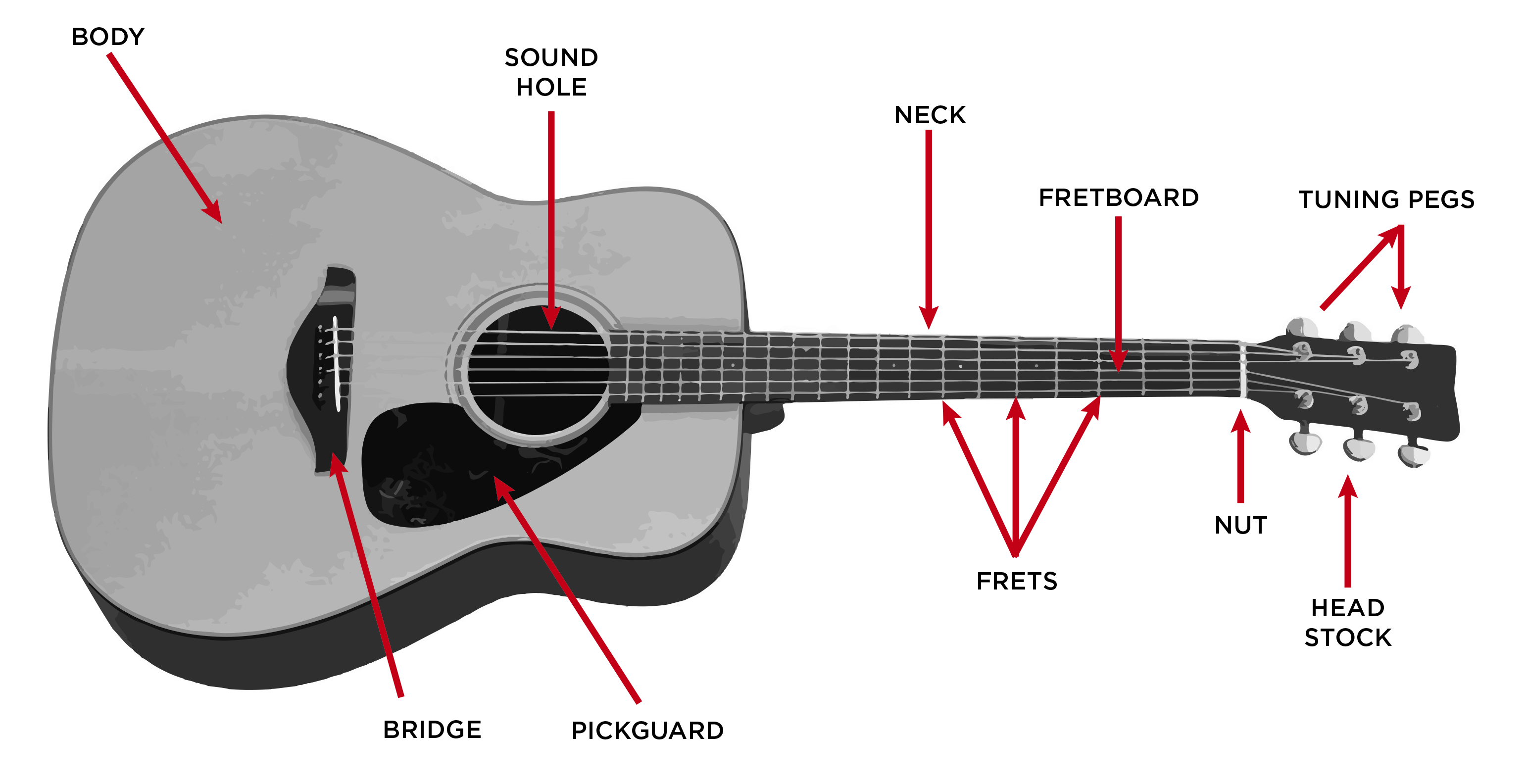
The Acoustic Guitar Step By Step Buying Guide GAK BLOG
Anatomy of an Electric Guitar Explained Headstock Body Pickguard Output Jack Neck Truss Adjustment Bolt Truss Rod Fretboard Frets & Fret Markers Strings Hardware Tuning Pegs Bridge and Saddle Nut String Trees Tailpiece Strap Buttons Vibrato System Onboard Electronics Pickups Pickup Selector Switch Volume and Tone Controls
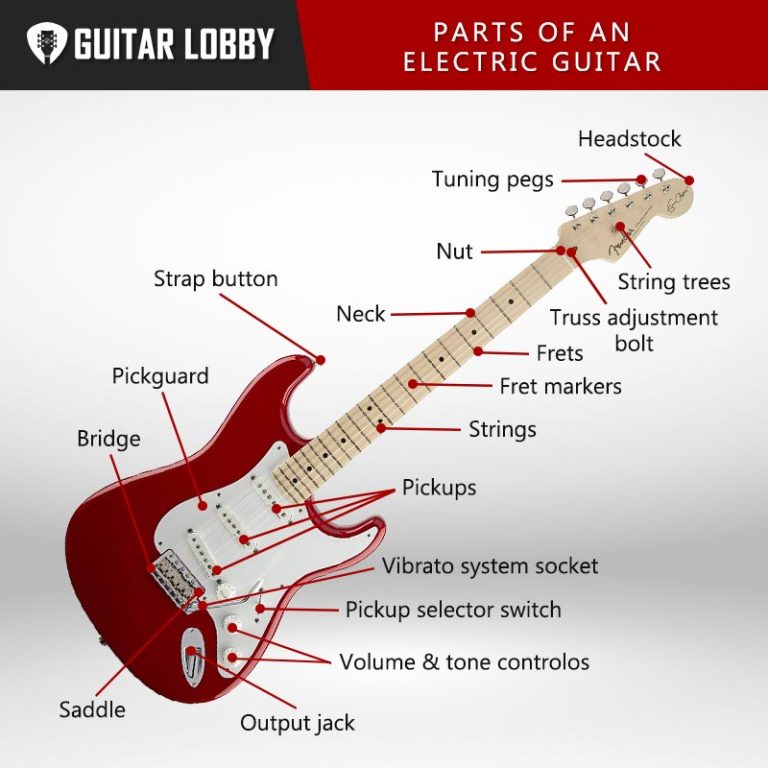
Parts of an Electric Guitar (with Diagram & Videos) 2023 Guitar Lobby
Acoustic Guitar Parts Diagram The below diagram shows two different acoustic guitars with the parts labeled. The guitar on the left is a steel string acoustic and the guitar on the right is a nylon string acoustic. While the two types of acoustic guitars are very different in how they sound and play, many of the parts are similar.

The Parts of an Acoustic Guitar Sound Pure
Overview This guide will outline the common anatomy of the electric guitar. The picture below shows three common styles of guitars. Even though they each look pretty different, they all share core components that allow them to function in the same way.

Acoustic Guitar Anatomy Diagram and Definitions
Bridge: The bridge is what keeps the strings of the guitar attached to the body. Like the nut, this is the other area of the guitar through which the vibration is passed, creating the tone of your guitar. It does also function as the place where intonation is set on an electric guitar, via a moving part called a saddle.
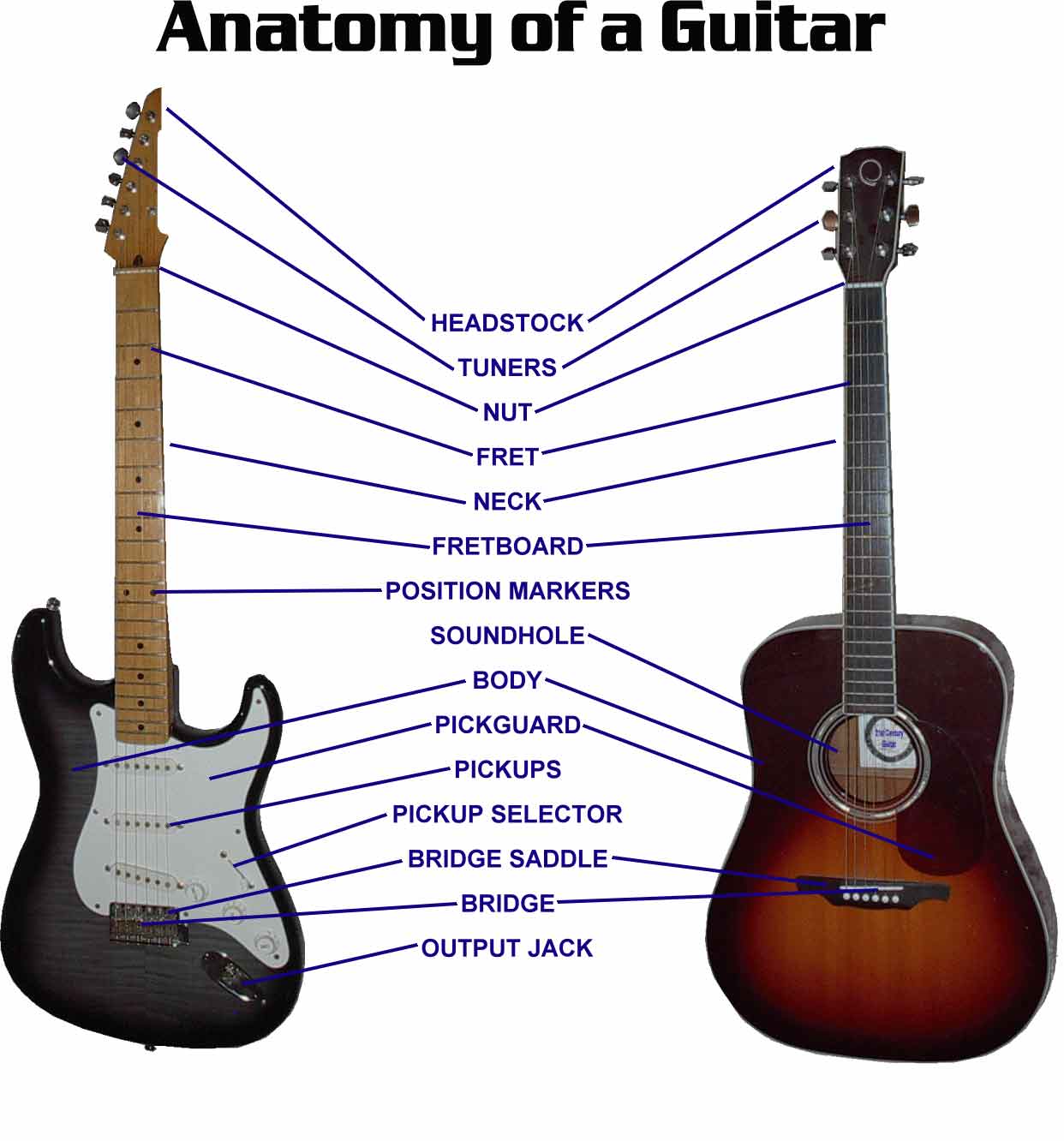
Guitar Gurukul Parts of a Guitar
The anatomy of an electric guitar consists of the body, neck, headstock, fretboard, frets, nut, tuning machines, strings, pickups, volume and tone controls, bridge, saddles, output jack, and other parts. You'll see all the various parts of the electric guitar in the following illustration. Electric Guitar Anatomy.

Guitar Anatomy 101 Parts Of A Guitar, Strings Labeled & Fret Numbering
Label the Guitar Printout. Advertisement. EnchantedLearning.com is a user-supported site. As a bonus, site members have access to a banner-ad-free version of the site, with print-friendly pages.. Label the Guitar Label the parts of a guitar. More Music Activities: Word Bank: bridge frets head hollow body neck pick guard (not on classical.

Parts Of A Guitar Explained (Acoustic & Electric Diagrams)
Guitar Parts Diagram - Main Parts Of The Guitar As illustrated in the diagram below, the guitar (like humans!) has a head, neck and body. The head or headstock is where you tune the guitar. The neck is where you hold the guitar in your left hand (if you're right handed) or your right hand (if you're left handed).